4 min read
Navigating the Future of the Pulp, Paper, and Packaging Industry
ResourceWise
:
Dec 9, 2024 12:00:00 AM
As the global landscape evolves, the pulp, paper, and packaging industry stands at a pivotal crossroads. Rapid advancements in technology, changing consumer preferences, and increased pressure for sustainability are just some of the factors that are shaping the future of this industry.
In this ever-changing landscape, it is important for businesses to stay informed and adapt to stay relevant. Here are some key areas to watch out for in navigating the future of the pulp, paper, and packaging industry.
Industry Trends: The Rise of Packaging and Tissue
Over the past 15 years, the global paper industry has undergone a significant transformation. Packaging and tissue products have emerged as dominant forces, reflecting shifting consumer demands and environmental concerns.
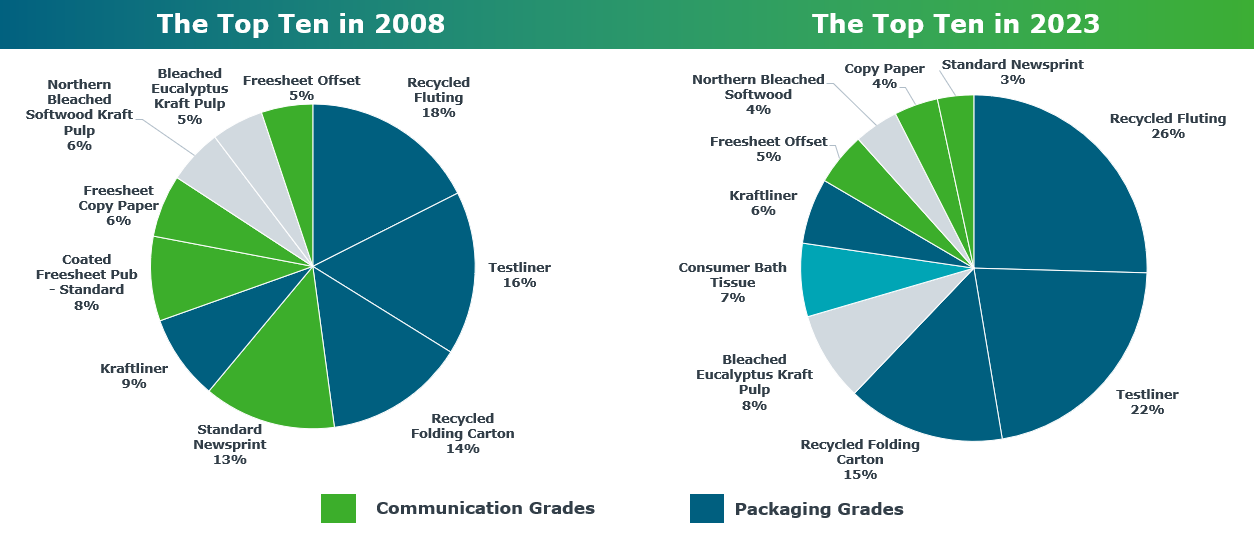
In 2023, recycled fluting, testliner, and recycled folding carton — all packaging grades —took center stage as top products, making up 63% of the top 10 grades. This was a notable shift from 2008 when standard newsprint and copy paper were more prevalent.
Top 10 Grades 2008 vs 2023

Source: FisherSolve
This transition underscores a broader trend towards sustainable, recycled materials in response to global sustainability pressures.
Overall, we haven't seen much change in the amount of capacity produced in Europe as it's remained relatively stable over the past years. We have however seen substantial changes in the product mix, as mentioned earlier. When analyzing the European market, FisherSolve data reveals that Türkiye will be adding most of the European containerboard capacity in the coming years.
Geopolitical Impact: Influences Shaping the Industry
Geopolitical dynamics play a crucial role in the pulp and paper industry. In particular, China's strategic capital investments have positioned it as a formidable player, with government support facilitating rapid industry growth.
Meanwhile, European regulations, such as the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), are reshaping operational landscapes by enforcing stricter compliance standards. These factors collectively influence market stability and competitiveness, prompting companies to adapt swiftly to remain viable.
The EUDR is a significant legislative framework aimed at tackling global deforestation and forest degradation. Implemented to ensure that products imported into the EU do not contribute to deforestation, the EUDR requires businesses to provide verifiable due diligence on their supply chains.
This means companies must demonstrate that the commodities they trade, such as wood, soy, palm oil, and coffee, are sourced from land that has not been deforested after a specific cut-off date, which is set for December 31, 2020.
The wood market is anticipated to feel the greatest impact from the EUDR, consequently affecting the pulp and paper industry. While the EUDR does not directly address recycled paper, its implementation may lead to a heightened demand for recycled materials. This, in turn, could drive up the demand and prices of recovered fiber.
So, which fiber-based commodities are most at risk for exporters?
The answer to that question differs by country. For example, China supplies nearly half of the recycled fiber imported by the EU for packaging boxes, while Brazil is a key provider of market pulp. Both countries contribute millions of tons. Additionally, the EU's reliance on imported market pulp has reached a level that puts production in numerous mills at significant risk.
Imports to the EU
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
If geopolitical tensions escalate, the construction of machinery worth billions within the industry could be jeopardized, potentially diverting business away from European suppliers. In Russia, the industry is increasingly turning to Chinese suppliers for spare parts and chemicals, a shift that diminishes EU revenues.
As a result, these companies must redefine their business strategies and objectives to secure socially legitimate sources and licenses for forest harvesting.
Additionally, the potential impact of the stricter trade restrictions proposed by the new US administration remains challenging to predict. Outcomes could range from widespread disruptions affecting numerous trade channels to minimal changes if the sanctions amount to little more than empty threats. Regardless of the scenario, businesses should closely monitor developments to stay prepared.
Future Outlook: Growth and Challenges Ahead
The future of the pulp and paper industry presents a mix of opportunities and challenges. By 2034, significant capacity expansions will be essential to meet growing global demand, particularly in containerboard, cartonboard, and tissue products. This raises critical questions such as who will drive this capacity growth, and where will it take place?
FisherSolve data reveals that since 2022, most new machine lines have been built in the Asia-Pacific and Latin America regions. The question now is whether these regions will continue to dominate capacity growth in the years to come.
New Machine Builds Since 2022
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
Despite these expansion opportunities, the industry faces considerable challenges. Regulatory compliance, geopolitical uncertainties, and sustainability pressures are shaping the landscape. For example, the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) enforces strict traceability and sustainability standards, pushing companies to innovate and adopt environmentally conscious practices. As the global market shifts towards sustainable solutions, navigating these complexities will be critical for long-term success.
China, a major player in the pulp and paper sector, faces its own unique challenges. To reduce reliance on imported market pulp, Chinese producers are increasingly investing in integrated pulp mills. Consequently, import volumes have remained relatively flat since 2024.
However, the expansion of fiber line capacity presents another hurdle: securing adequate wood chip supplies. Currently, China imports nearly 50% of the hardwood chips needed for its pulp and paper production. This dependence raises pressing questions about the sustainability of supply sources, particularly in light of EUDR regulations.
Meanwhile, in Europe, the pulp and paper industry is grappling with overcapacity and uncertain demand. Many previously announced projects are facing delays, cancellations, or indefinite postponements. For instance:
- Heinzel’s product change project at its Laakirchen site has been delayed by several months.
- The restart of Norske Skog’s line at its Golbey site has also been postponed.
To thrive in this evolving industry, stakeholders must address these challenges head-on, balancing growth ambitions with sustainability, regulatory compliance, and resource constraints.
A Path Forward
The pulp, paper, and packaging industry is poised for transformation as it addresses emerging trends, geopolitical influences, and environmental challenges. By embracing innovation and sustainability, the sector can adapt to evolving demands and maintain its vital role in the global economy. As the industry navigates this complex landscape, its ability to balance growth with ecological stewardship will be paramount to its continued success.





