5 min read
The Growing Tissue Sector in the Middle East: Opportunities and Challenges
 Bruce Janda
:
Oct 5, 2023 12:00:00 AM
Bruce Janda
:
Oct 5, 2023 12:00:00 AM
The Middle East stands as a prominent birthplace of human civilization, with shared linguistic and religious origins. However, enduring differences and disputes that have simmered for centuries and even millennia continue to hinder the development of pan-regional cooperation within its tissue sector. It is politics, rather than geography, that dictates economic collaboration and trade within the region. Therefore, an analysis of tissue demand and production in the area must take into consideration these factors.
Exploring the Components of the Middle East
The Middle East is a region with complex and fluid boundaries. Its component countries are defined more by political factors rather than geographical ones, leading to varying definitions. Different statistical sources use different criteria to define the countries in the Middle East. In this report, we consider Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, the Palestinian Territories, Saudi Arabia, Syria, the UAE, and Yemen as the component countries of the Middle East.
Table 1 provides a comprehensive overview of the distinct characteristics found within the region, according to World Factbook. Economic and trade rate data is more difficult to obtain in closed societies. Some of these figures are the best estimates of the source noted. In this case, the Palestinian Territories are broken separately as Gaza and West Bank. Data shown in the table are mostly 2023 estimates and go no earlier than 2021, except as noted for Syria and Yemen.
Table 1: Middle East Economic Statistics Supporting Tissue Demand Growth

The disparity between rich and poor countries in the Middle East is shocking and probably the result of the current and historic conflicts. Despite this, tissue demand and production continue to increase. Several factors that drive the growth of the tissue industry in the Middle East include:
- The growing population and disposable income. The Middle East is one of the fastest-growing regions in the world, and the population is expected to reach over 600 million by 2050. This growth is accompanied by an increase in disposable income, making tissue products more affordable for more people.
- The increasing awareness of hygiene and sanitation. There is a growing awareness of the importance of hygiene and sanitation in the Middle East. This leads to increased use of tissue products for personal hygiene and cleaning.
- The rising demand for tissue products from hotels, restaurants, and other businesses. The tourism industry is increasing in the Middle East, driving the need for tissue products from hotels, restaurants, and other companies.
However, it’s important to acknowledge some headwinds that impair the development of a robust regional tissue sector, such as:
- Lack of access to recycled paper. The Middle East lacks robust access to recycled paper, a primary raw material for tissue production. This forces tissue manufacturers to rely on virgin wood pulp, which is more expensive.
- Competition from imported tissue products. Some global tissue manufacturers are setting up production facilities near the Middle East to take advantage of the growing market. This is increasing competition for local tissue manufacturers.
We last discussed this region in 2021 during the pandemic. Since then, the Russian invasion of Ukraine has further divided the area and boosted energy exporters. A map of the Middle East region is shown in Figure 1. Tissue mills are shown as pin markers. Egypt is an African tissue maker but continues to be part of the cultural and economic ties of the Middle East.
Figure 1: Middle East Tissue Map
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
Import and Export Trends
Tissue imports into the region are shown in Figure 2. Turkey and Indonesia are significant sources of tissue imports, with smaller amounts from China and Italy. Egypt is counted as a producer in the region, but it would be a substantial source on this supply chart if broken out separately.
Figure 2: Middle East Tissue Imports Trend

Source: FisherSolve
Tissue product exports from the Middle East are shown in Figure 3. The enormous export contribution of Egypt tends to overshadow the other producers. A study of the intra-Middle East tissue trade would be complicated enough to merit a separate article. However, except for Egypt, relatively little tissue is exported from the region.
Figure 3: Middle East Tissue Exports Trend
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
Emerging Tissue Developments in the Middle East
Egypt, Iran, UAE, and Saudi Arabia are the overwhelming heavyweight producers in the region. Iran and Saudi Arabia have also announced significant new tissue projects that are to come online in 2024-25. However, Lebanon, Israel, and Jordan have lost capacity over the trend period shown. Iraq discontinued production in 2012. The trend of tissue machine count changes is shown in Figure 4. Note the forecast increase in 2024. The number of machines can be misleading as the new machines coming in tend to be much larger and faster than the old ones that were shut down.
Figure 4: Middle East Tissue Machine Fleet Count Changes
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
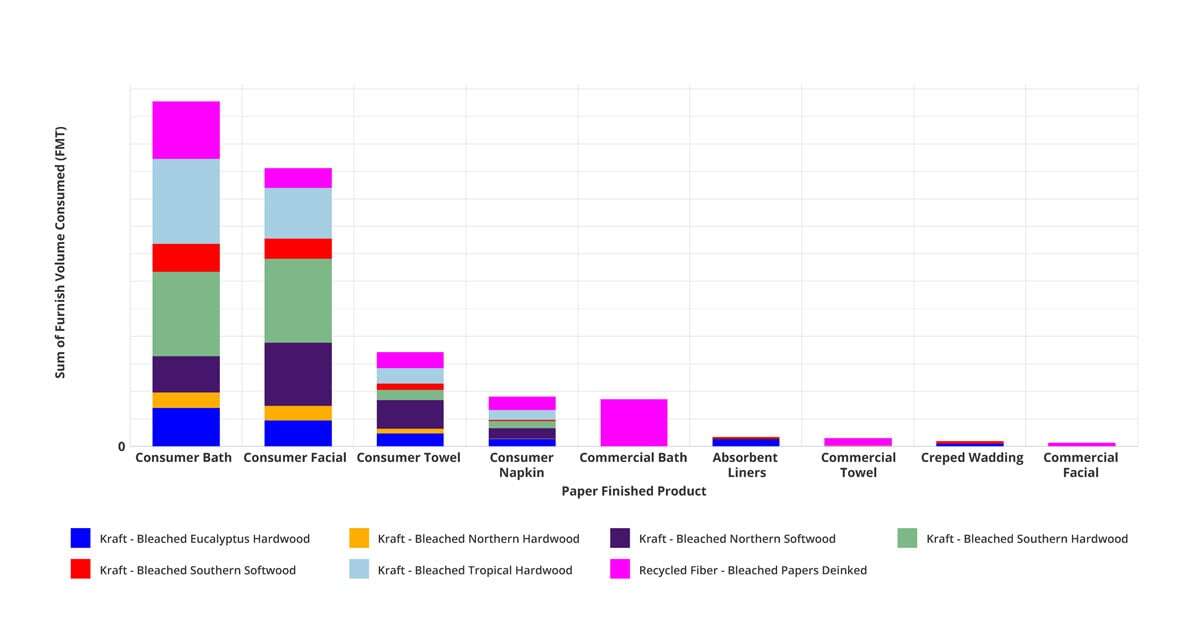
The region’s tissue fiber use for each finished product is shown in Figure 5. Some eucalyptus and other tropical hardwoods are used in the consumer grades. Relatively little recycled fiber is used, except in commercial bath. Some producers have work underway to increase the use of low-cost recycled fiber.
Figure 5: Middle East Tissue Furnish by Finished Product

Source: FisherSolve
The exact breakdown by finished tissue product is shown in Figure 6. Here, the colored bar segments represent each country's tissue production mix. Most countries tend to make the same product range, but Iran specializes in absorbent liners and creped wadding.
Figure 6: Middle East Tissue Finished Products - Production by Country
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
A Side-by-Side Comparison of the Countries
The quality of the Middle East’s tissue machine fleet is shown in Figure 7. The size of the bubble for each country represents the relative production capacity. The X-axis represents the average technical age, and the Y-axis represents the average machine width. This tends to track well with average machine speed in most cases. Turkey is the leading tissue exporter on the border of the region and was included here for comparison.
Figure 7: Middle East Tissue Machine Quality Comparison
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
Saudi Arabia and Iran are poised to become bigger bubbles with younger and wider machines. Kuwait appears to be in a weak position.
The average cash cost for tissue production is shown in Figure 8. Turkey, Italy, and Indonesia are established tissue exporters to the Middle East and are included to help define their competitive position in the region. Surprisingly, many countries within the region have similar production costs and are not far behind Indonesia, the cost leader. Turkey and Italy are slightly higher, but they may well provide preferred product performance.
Figure 8: Middle East Tissue Comparison - Average Cash Costs

Source: FisherSolve
The tissue machine average viability by country is shown in Figure 9. FisherSolve's Viability Index provides valuable insights into the relative viability and potential success of tissue machines in the Middle East region. It offers an exclusive ranking system that assesses the future competitive position of each tissue machine based on factors such as capital requirements, cost, size, and technological age.
Now, the region’s tissue production shows more differences. The UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Egypt, and Bahrain are all in the lowest viability zone with low-risk Turkey and Indonesia. Jordan and Syria are in an elevated risk zone with Italy. Israel, Lebanon, and Kuwait are relatively high-risk and require investment to keep pace.
Figure 9: Middle East Comparison Set - Tissue Machine Viability
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
Figure 10 provides a view of carbon emissions per ton of production for the comparison set. This chart was based on a cradle-to-gate methodology and includes the carbon content of raw materials. Kuwait and Israel stand out as high emitters, followed by Jordan, Syria, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, and Bahrain. All the others have some differences in emission composition but possess very similar emission totals. The new Saudi Arabian projects may help change this.
Figure 10: Middle East Carbon Benchmark – Cradle to Gate
 Source: FisherSolve
Source: FisherSolve
In Summary...
Overall, the tissue industry in the Middle East is a dynamic and growing market despite the political and social barriers. Further peace movements could help accelerate this growth. While the industry is encountering certain challenges, it is also strategically poised for expansion. Through sustained investment and innovation, the tissue industry in the Middle East has the potential to emerge as a significant contender in the global market. As concentrated investments steer the future, not all countries involved in tissue production will maintain their prominence. Instead, attention is shifting towards smaller producing nations, including the United Arab Emirates, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Bahrain.
To truly understand the competitive landscape of the tissue industry in the Middle East, it is essential to dive into the specifics of tissue producers and individual machines. While this article provides a comprehensive overview of the region's tissue industry, it is important to note that visibility may be limited in certain countries due to internal and political challenges. Factors such as fiber prices, exchange rates, and environmental regulations are also constantly evolving, presenting both advantages and new challenges for industry players. Additionally, the landscape of tissue mills in the Middle East is expected to undergo further changes as mills change ownership and consolidate. Moreover, neighboring countries may also invest in their own tissue-making capacity, which could impact the region's imports and exports.




![[Video] Molecules to Markets Episode 1: Chemical Markets Begin 2026 in a Supply-Driven, Margin-Sensitive Environment](https://www.resourcewise.com/hubfs/images-and-graphics/blog/chemicals/2026/weekly-video-series-molecules-to-markets/CHEM-Weekly-Video-Series-Molecules-to-Markets-Episode-1.png)
