In line with other nations targeting fiscal policy to kickstart economic growth, China has plans to cut interest rates by the close of October 2024. This could be just the kind of post-COVID-19 hangover stimulus package the Chinese economy—arguably the world's largest in terms of consumption and production—needs.
Similarly, reducing bank deposit reserve ratios gives monetary institutions the freedom to issue new loans. This can, in turn, hold the potential to trigger economic activity.
Likewise, lower new mortgage interest rates can rouse housing markets from the doldrums. Or, the disposable income consumer markets are crying out for could be found by reducing down payment ratios on second homes...
Additionally, China's government may provide financial support to local governments to purchase unsellable properties. Plans to inject ¥800 billion (US$112-plus billion) into the stock market have already been announced.
A stimulus package is just the ticket to revive the world's biggest economy, right? Well, we took a deep dive into the matter and asked around. Here's what we found...
A dwindling Chinese economy means less income for other countries. The US, for example, exports around $150 billion worth of goods to China.
George West founded Chemical Intelligence, a US-based price reporting agency focused on glycols, methanol, and solvents that ResourceWise acquired a year ago.
West, now a director within the ResourceWise Chemicals division, sees direct correlations between China's and the outside world's economic fortunes.
 "In the monoethylene glycol (MEG) market, China remains the dominant consumer and, more recently, producer.
"In the monoethylene glycol (MEG) market, China remains the dominant consumer and, more recently, producer.
"What happens in China directly impacts other major trade centers. The Americas and Europe respond to supply and demand fluctuations within China's market. Economic malaise there materially depressed global MEG markets. Restocking ahead of the recent National Day of the People's Republic of China holidays (October 1) drove prices up.
"Downstream, cheap PET and polyester continue to flood into overseas markets. That dynamic appears likely to continue," West adds.
Methanol Markets
China is the largest consumer and the largest producer of methanol. "Changes within the country's methanol markets, however, have less of an impact on other major centers of trade, which remain somewhat insular.
"Stimulus measures should bolster demand in China and eventually help support the global market. That said, prices and margins are already relatively high partly due to relatively low raw material costs, especially in insular markets such as those in the Americas," West adds.
Following Japanese Footsteps...?
International backers of Chinese equities are hoping that President Xi Jinping will roll out a raft of fiscal spending and reforms that have the desired effect.
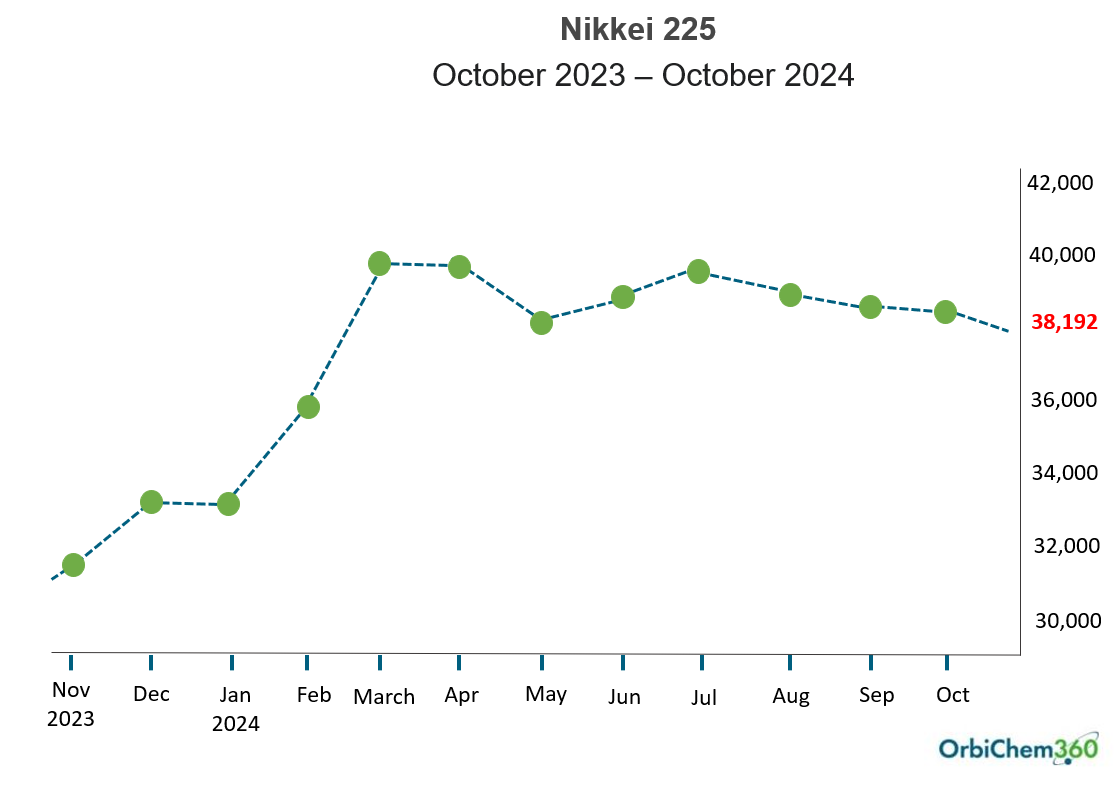
It appears the Japanese government's recent measures to make its stock market more attractive to foreign investors have worked. The Nikkei Index saw huge hikes, reaching its highest-ever position in February 2024 following the use of fiscal policy levers to drive growth. The graph below does not show peaks and troughs within a month-period, for example, when Nikkei 225 slumped on news that the US recovery was faltering early in August.
The graph below reflects the morning of October 23, 3024. It shows the Nikkei 225 stock market index—which tracks the country's top 225 companies traded on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. The indication is that Japan is experiencing the end of deflation.
China's neighbor is seeing the kind of return to steady growth that the People's Republic and its trading partners need.


Post-stimulus Thinking
But thus far, Europe feels there will be little difference. "I'm told by those in the market that these measures will not be enough to have a huge impact," reports Regina Sousa, Senior Consultant at ResourceWise Chemicals.
"Some boost in market confidence was expected in the short term after the news, which could lead to better demand," adds Sousa. There is, however, a need for long-term change.
Positivity So Far
There have indeed been some positive changes in the market regarding confidence following the Chinese government's announcement of its economic stimulus package. However, the effects and impacts are still unfolding.
Below are a few notable changes:
- Accelerated investment and start-up of infrastructure projects: Government stimulus packages usually lead to faster start-up of infrastructure projects, especially in transportation, energy, and urban construction. Such projects can increase employment and boost demand for related industries such as steel, cement, and construction equipment, thus energizing the economy.
- Rebound in the real estate market: In response to the downward pressure on the real estate market, the Government may take measures to support the sector. Looser monetary policy and more flexible mortgage policy could lead to a short-term rebound in the real estate market, especially in large and medium-sized cities.
- Consumption and business confidence boost: Government stimulus policies can boost consumer confidence through tax cuts and fee reductions, as well as higher disposable incomes for residents. At the same time, policy incentives make enterprises more optimistic about future development, which helps to increase the incentive for production and investment.
- Financial market volatility and monetary easing: To support economic growth, the People's Bank of China may adopt monetary easing measures, such as lowering interest rates or increasing market liquidity. Such monetary policies usually lead to short-term stock market gains, especially in sectors related to consumption, technology, and manufacturing.
- Manufacturing and export recovery: With the global supply chain recovering, the Government has promoted the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing sector through subsidies and supportive policies, and capacity has been restored in some sectors. In addition, export-oriented enterprises can benefit, especially if global demand stabilizes or recovers.
However, some constraints and challenges exist. While the economic stimulus measures may bring some market improvement, it remains to be seen whether they can truly stimulate economic growth and structural adjustments in the long run.
For example:
- Indebtedness and inflationary pressures: Over-reliance on government spending and credit expansion may increase pressure on government indebtedness while potentially pushing up inflation.
- Demand deficiency issues: China's external demand faces uncertainty due to the slowdown in global economic growth, and the consumer market has been slow to recover, all of which could affect the pace of overall economic improvement.
Overall, the government's economic stimulus policies have brought short-term signs of market improvement, including an immediate slight price uptrend in acrylic monomer values that are considered likely to be linked to the measures.
However, real economic recovery must be supported by long-term structural reforms and sustained domestic demand growth.

 Jane Denny
Jane Denny


![[Video] Molecules to Markets Episode 1: Chemical Markets Begin 2026 in a Supply-Driven, Margin-Sensitive Environment](https://www.resourcewise.com/hubfs/images-and-graphics/blog/chemicals/2026/weekly-video-series-molecules-to-markets/CHEM-Weekly-Video-Series-Molecules-to-Markets-Episode-1.png)
