6 min read
Chemicals A-Z: Acetyls to Xylenes Ten Years to Q4 2024 (The Series)
 Jane Denny
:
Nov 7, 2024 12:00:00 AM
Jane Denny
:
Nov 7, 2024 12:00:00 AM
As the global chemicals industry adjusts to pervasive oversupply versus dwindling demand, we dig into our 10-year archive of price points for over 100 chemicals to demonstrate how times have changed.
In this special investigative series, we examine pricing structures across the full range of chemicals in our portfolio, beginning with acetyls and acrylates. How do their prices compare now with November 2014? Which chemicals are demonstrating price rises in Q4 2024? And why?
Are price points and indexes mirrored across the globe? And if not, how do they differ? A six-part series, Part II will examine aromatics, acrylonitrile, olefins, orthoxylene, and phthalic anhydride this November. Part III will be dedicated to caustic soda, chlorine, and its derivatives.
Part IV will explore plastics and resins, including fibers, feedstocks, and additives vital to output. Worth at least a trillion dollars per annum and with an output of hundreds of millions of tons every year.
Part V will focus on maleic anhydride, olefins and polyurethanes. The final part will critically examine the findings of the prior five to provide insight into where markets might go next.
Methanol in the Market
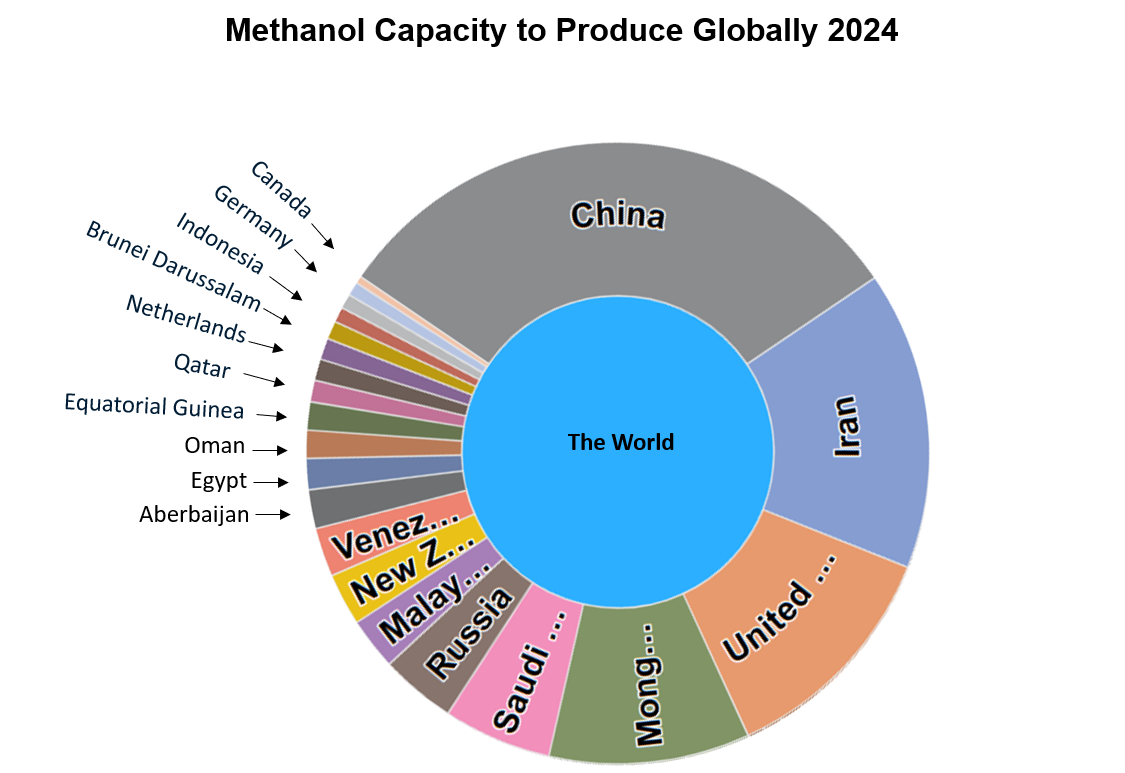
According to the ResourceWise glycols, solvents, and methanol-focused price and analysis platform ChemEdge360, the capacity to produce methanol globally is almost 90,000 ktpa in 2024, with China as the primary production hub.

Source: Adapted from ChemEdge360
Methanol is an important primary chemical product, used as a chemical feedstock for production of a range of important industrial chemicals. A key acetyl chemical—acetic acid—and the acrylate methyl methacrylate (MMA) both require stable supply and price structures from methanol markets to maintain healthy business outlooks.
Methanol remains among the world’s largest-volume chemical feedstocks. However, as the infographic above shows, Europe's methanol output is almost negligible compared to other regions and countries. Rising natural gas prices have put paid to Europe's output in recent years, and the impact on its price in the region is notable.
However, despite the US having ample capacity to supply markets—in fact, well over 10,000 ktpa as of 2024—prices there escalated this past year. Partly, this is due to chemical sector buyers being forced to compete with biodiesel producers. Global markets for biodiesel—a renewable fuel produced by the chemical reaction of methanol and vegetable oils or animal fats—are monitored by ResourceWise with prices, insight, and analysis available on our PrimaCarbonZero platform.
The biofuels sector has been heavily subsidized since former President Biden's Inflation Reduction Act incentivized renewable fuel production to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Overall, our chemical intelligence platform OrbiChem360 includes 14 prices in its methanol series. All of the prices, including those included in the graph of selected prices below, have migrated upwards since mid-2024, with most prices in the series rising consistently since 2023.

Source: OrbiChem360
An American Tale
A US-focused price series within our ChemEdge360 platform paints a similar picture, as seen in the graph below. Since most acetic acid is produced by methanol carbonylation—in which carbon monoxide is introduced to the chemical production process—higher methanol prices have a direct impact on margins for acetic acid-derived products, including vinyl acetate monomers (VAM).

Source: ChemEdge360
Acetyls Under Analysis
Key to chemical intermediates used in paints, coatings, and adhesives, the acetyls subsector includes butyl acetate, ethyl acetate, VAM, acetic acid, and acetic anhydride.
Industries, including hygiene, pharmaceuticals, food, and agriculture sectors, rely on acetyl feedstocks.
Of all the acetyl products monitored by ResourceWise, acetic acid is the most abundant. Global capacity is currently around 23,000 ktpa. Over half is produced in China, where more is expected online in the coming years. In percentage terms, the annual growth rate for the 2020s is highest in North America at 4.4 percent. But, the region's overall output today represents just 16 percent of the global total.
The lowest price point for acetic acid globally today—as per OrbiChem360—is a Chinese acetyls market index: so low, in fact, that it is below the product's lowest recorded price (also a Chinese price index) during 2014—though marginally, at 5 percent lower.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, acetic acid's highest price in Q4 2024—West Europe Bulk DDP Contract price—is lower in 2024 than 2014 too. At around 25 percent lower than the product's 2014 peak price—a North American Domestic Bulk FOB price—the margin of difference between the price at the 10-year gap is much larger.
Vinyl Acetate Monomer (VAM)
Various polymers and resins are made using the versatile chemical building block VAM, including some used in solar panels. In fact, buoyant solar energy markets triggered by rising natural gas prices increased demand for VAM this decade. We explored this subject in our blog post, Solar Energy Boom Sparks Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Capacity Expansion.
With global energy think thank Ember research indicating 2024 a bumper year for the solar industry, extra VAM capacity may help ensure production costs remain competitive for the renewable energy sector.
Currently, over half the world's VAM capacity is located in Asia, with nearly one-fifth manufactured in North America. All the world's trading regions—except Europe, the Middle East, and Africa (EMEA)—plan to increase capacity in the coming half-decade. In fact, China's 2020s VAM growth rate is forecast at 6.6 percent, according to OrbiChem360 data.
In all, the OrbiChem360 VAM price series comprises 11 price points from Asia, Europe, and North America. As the graph shows, Europe's VAM prices are elevated compared to the rest of the world.

Source: OrbiChem360
During demand downturns, such as seen in the trading bloc and globally today, that might not be expected. However, not only have rising energy costs and volatile crude oil markets contributed to higher prices in spot markets, but contract prices remain high, too. It can be the case that even when demand is low, upstream producers maintain relatively high contract prices to ensure they cover their own costs for maintaining plant output at all.
As the global chemicals market shifts to adjust to changing supply and demand dynamics, we've listed plant closures globally.
Over 10,000 kilotons per year of chemical capacity has been cut from chemical value chains during the 2020s. Download our white paper to find out more...
Pre and Post-pandemic Acrylics and Acrylates
Global acrylic and acrylate market participants have been longing for a phenomenon that will trigger demand, as COVID-19 did, without the risk to human health, of course. The pandemic brought renewed purpose to an industry reliant on buoyancy in traditional market sectors. Transparent plastic screens were all the rage, and while producers might have struggled to find feedstocks, they knew the price point for their product would be high. Banks, supermarkets, and, indeed, the majority of customer-facing businesses required protective screening to operate effectively.
As the world emerged from the modern-day plague, these markets had little direction. Even the auto and construction sectors—and the need for headlights and bathroom suites, respectively—remain deep in the doldrums as of Q4 2024.
Methyl Methacrylate Markets
As of Q4 2024, methyl methacrylate (MMA) markets globally have taken a tumble. As the graph below shows, some fairly significant price increases were seen in MMA markets earlier this year. In H2 2024, even that fell to flatness, and now, price dips are being seen across the board.

In November 2020, Mitsubishi Chemical announced plans to end MMA monomer and methacrylic acid output at its subsidiary Lucite International's site in Texas, US, which happened in February 2021. This resulted in a tighter North American market for those products as other regional manufacturing units were aged and unreliable, while new investments were well off the pace.
In fact, the upward pressure on prices in both Europe and the US is a recurring theme, says Jaroslaw Cienkosz, Consultant ResourceWise Chemicals. As Cienkosz shared in our blog post earlier this year, Industry Litmus Test: Insight from a Chemical Consultancy Team at Large: "Low global output and the consequent shortages—alongside high quotations for MMA—started in Q2."
“The start-up of Röhm’s new plant in Texas is unlikely to resolve all issues in the sector,” Cienkosz adds. Mitsubishi's deferred final investment decision for its 350 ktpa MMA plant in Geismar, Louisiana due to market volatilities is indicative of the challenges the industry faces.
Electric Vehicle Market Promise
One promising area of development for poly(methyl methacrylates)—or PMMA—is the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) sector. Technically a thermoplastic, PMMA is a lightweight and smash-resistant substitute for glass in many applications.
In EV manufacturing, a material that can meet the same requirements as glass (or exceed them) minus the extra weight presents a valuable proposition. PMMA weighs half as much as glass and allows more light to pass through it than glass.
While PMMA windscreens are not as common as glass in traditional automobile windscreen manufacturing, German specialty chemicals company Evonik supplied RED Motorsport's Lotus race car with a design made using Plexiglas, nowadays owned by Darmstadt, Germany-headquartered Röhm and supplied by Polyvantis.
The use of ammonia in PMMA upstream production is one matter of importance going forward. Using ammonia feedstocks to make products makes the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism relevant.
Though not live until 2026, producers will be required to account for and buy CBAM certificates equated to the cost of the carbon emitted during the goods' production cycle. Account will be taken of any carbon emission premiums paid within the producers' country. The price of the certificates will be calculated depending on the weekly average auction price of EU Emission Trading Scheme allowances expressed in Euro/ton of CO2 emitted minus any premiums paid in the originating country. Market participants prepare for this by introducing bio-ammonia for the production of the PMMA precursor MMA. Nitrogen, methanol, and hydrogen producer and distributor OCI Global and Röhm co-developed a pioneering process to produce MMA using bio-ammonia.
The Final Quarter
As the final quarter of 2024 proceeds, producers across petrochemicals value chains will be assessing future viabilities and opportunity. Insight into market trends, closures, divestments and adaptations of traditional fossil fuel-based business will be vital to market participants.
Stay up to date by subscribing to our newsletter.





![[Video] Molecules to Markets Episode 1: Chemical Markets Begin 2026 in a Supply-Driven, Margin-Sensitive Environment](https://www.resourcewise.com/hubfs/images-and-graphics/blog/chemicals/2026/weekly-video-series-molecules-to-markets/CHEM-Weekly-Video-Series-Molecules-to-Markets-Episode-1.png)
