4 min read
Acetone Anti-dumping: Volatility in Protectionist Markets (Part 1)
 Jane Denny
:
Sep 3, 2024 12:00:00 AM
Jane Denny
:
Sep 3, 2024 12:00:00 AM
As a chemical intermediate in the production of acrylics and polycarbonates, and key solvent compound, acetone underpins a wide range of end products.
Traditionally made from calcium acetate distillation, Russian-born biochemist Chaim Weizmann disrupted that with a fermentation process around a century ago. He converted corn and potato starch to acetone and butyl alcohol using bacteria. Weizmann's acetone–butanol–ethanol plants, or ABE plants as they were known, operated throughout the UK and North America.
ABE plants lost ground to a cheaper solution, the dehydrogenation of petroleum-derived isopropanol, during the 1930s, before the Hock process emerged in the 1950s. As per the Hock route, benzene and propylene are converted to phenol, with acetone as the co-product. It is this mutuality that renders phenol demand a key acetone market fundamental now.
 Ashely Rock, Senior Market Analyst ResourceWise Chemicals (pictured right), monitors aromatics alongside a range of solvent-focused chemicals.
Ashely Rock, Senior Market Analyst ResourceWise Chemicals (pictured right), monitors aromatics alongside a range of solvent-focused chemicals.
Rock notes that acetone and phenol co-dependency is currently at play in US markets.
“With demand for phenol low at present, producers have curtailed operations. In the US, output is currently around 60 percent of nameplate capacity," says Rock.
Demand for acetone's co-product, phenol, remains weak as the economic downturn has impacted industries that require phenolic feedstock. The epoxy resins sector, for example, needs a healthy housebuilding and construction sector to thrive.
And, US housing starts continue to demonstrate the freefall that began in 2021 and 2022, depending on the size of the development.
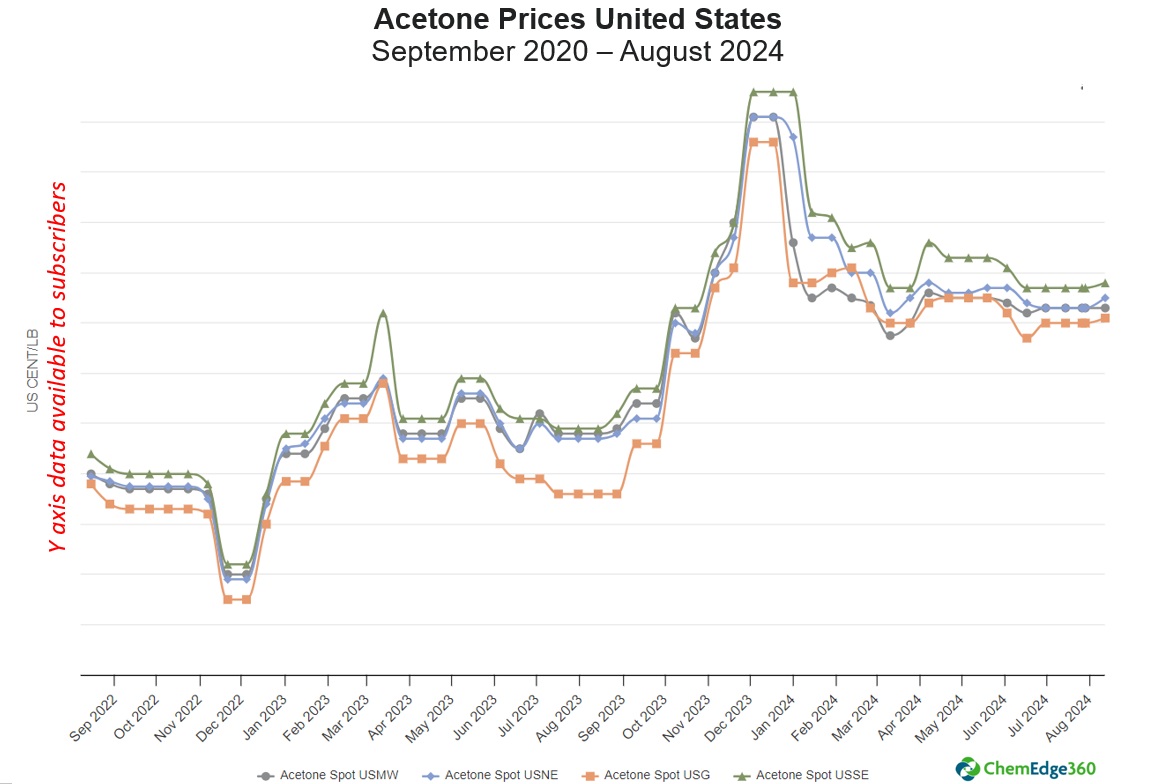
Less phenol means less acetone, and consequently, acetone prices are higher. As shown in the graph below, acetone prices are prone to volatility. Recent settlements, however, show an uptick in all except one—acetone spot in the US Midwest—which has remained stable since the start of July.

Source: ChemEdge360
Anti-dumping and Acetone Availability
At the start of the 2020s, New Jersey-based AdvanSix, Ohio-based Altivia Petrochemicals, and Missouri-based Olin triggered an anti-dumping investigation against Belgium, South Korea, and South Africa. The estimated value of imports to the US from the trio of acetone-producing counties was over US$130 million in 2018.
Dumping and Anti-dumping Defined
Dumping occurs when imported products are made available to buyers at prices lower than “normal value”—defined as its price in the exporter's own country or other countries. It may also be on a constructed value based on its production costs plus an amount for profit
Investigations are triggered when domestic producers raise concerns about the prices of foreign goods sold in their domestic markets.
When an investigation determines that dumping has occurred, measures are put in place to mitigate the problem in future. They usually constitute levies imposed on imported goods. These "taxes" compensate for the difference between their export price and their normal value.
Anti-dumping duties are usually not applied retrospectively. However, if imports suddenly rise in the 90-day period before publication and application of provisional remedies, retrospective duties will often be considered.
The anti-dumping duties imposed by the US Department of Commerce ranged from 28.10 percent for imports from Belgium up to 414.92 percent from South Africa's chemicals and energy company Sasol. Other South African acetone producers were subject to 314.51 percent anti-dumping duties.
South Korea's dumping margins were calculated at 25.05 percent for LG Chem and 47.86 percent for Kumho P&B Chemicals (KPB).
All anti-dumping measures were set to expire in 2025. However, rumors of Belgian and South African measures being extended are rife, according to Rock, a possibility she considers "absurd".
"US markets are short on acetone supply because output has been reduced due to weak phenol demand. Domestic producers are making very healthy margins off the back of decisions designed to limit Asian imports into the country," explains Rock.
South Korea Sellers Now Exempt
The investigation and ruling related to dumping activity occurring from January 1 to December 31, 2018. It was found that over 20 percent of South Korean-produced acetone had met the anti-dumping test.
Essentially, that meant that during the period of review, products sold for less than South Korea's cost of production plus a reasonable profit margin. While the US focused on KPB and LG Chem, anti-dumping duties of 33.10 percent were set for "all other" South Korean exporters.
The US government's Federal Register reported that the International Trade Administration determined KPB and LG Chem dumping margins for the year up to the end of February 2022 at zero.
Following that review of trade, South Korean producers became exempt from duties earlier this year.
 Hyunmin (Min) Kim, Senior Consultant, ResourceWise Chemicals (pictured left), says South Korea's producers are acutely aware of the precarious nature of the country's freedom to import to the US.
Hyunmin (Min) Kim, Senior Consultant, ResourceWise Chemicals (pictured left), says South Korea's producers are acutely aware of the precarious nature of the country's freedom to import to the US.
"Depending on this year's sales records, duties might be reimposed next year. Acetone producers, therefore, are extremely careful not to sell acetone at low prices.
They emphasize the importance of being cautious to avoid being subject to dumping duties."
Acetone: A Pivot on Propylene Price
Not only does the Hock process tie the price of acetone in with phenol demand, but liquidity in propylene markets underpins acetone's price stability, too. And that, as the price graph for chemical and refinery grades of propylene below shows, is a tall order.
Volatility in propylene markets is a given, with North American markets no exception. The graph demonstrates how, with the oil price drop after mid-2014, propylene prices followed suit, as would be expected.
Generally, the price of propylene rose as countries emerged from COVID-19 restrictions in 2021, and demand suddenly exceeded expectations. The Big Freeze in Texas in 2021 severely impacted olefins output. Russia's invasion of Ukraine in 2022 precipitated price rises due to volatility in energy markets.
While dwindling global oil inventories and geopolitical tensions play a part in propylene price fluctuations, its supply and demand fundamentals have traditionally been impacted by its co-product status, namely with ethylene.

Source: ResourceWise
Acetone Output in China
In China, 1300 ktpa of new acetone production came onstream since the start of the 2020s. Increases in bisphenol A, epoxy resins, and polycarbonate output have also occurred.
As in various other subsectors of the chemicals industry, China's new capacities have come onstream as domestic demand fell. Consequently, average run rates across both new and established facilities remain low because of weak demand for phenol.
The country's intense and prolonged COVID-19 restrictions and depressed housing market are key to this scenario. Whereas China once imported high volumes of acetone, domestic supply is sufficient. Erstwhile producers are now seeking alternative markets.
Acetone Markets of the Future
Along with all fossil fuel-based chemicals, the acetone market is set for disruption. Sustainability-focused regulation and legislation targeting the acrylic plastics, polycarbonates, and epoxy resin industries are inevitable. That is a "when," not "if" issue to ponder.
Will ABE technology enjoy a renaissance when petrochemical feedstock-based manufacturing dwindles? Perhaps some other more sustainable route to acetone output is waiting in the wings?
When the battle for customers relies on composition, will anti-dumping strategies endure? Or will the scramble for acceptable feedstocks cancel out such strategies to the annals of history for a while?
In the second part of this blog series, we will explore emerging technologies and recent attempts to reinstate ABE-based production.
To receive a notification email when our next blog and others go live, sign up for our chemicals-focused newsletter below.




![[Video] Molecules to Markets Episode 1: Chemical Markets Begin 2026 in a Supply-Driven, Margin-Sensitive Environment](https://www.resourcewise.com/hubfs/images-and-graphics/blog/chemicals/2026/weekly-video-series-molecules-to-markets/CHEM-Weekly-Video-Series-Molecules-to-Markets-Episode-1.png)
