2024 was a challenging year for the European plasticizers market with demand failing to pick up. Key end markets remained subdued as economic activity remained in the doldrums.
The year was characterized by slow construction activity across the continent. The automotive industry saw its outlook worsen as the year progressed. Consequently, there were plant closures, and demand remained below par.
In this economic landscape, plasticizer prices were largely influenced by fluctuations in feedstock markets, most notably 2-ethylhexanol (2-EH).
Rachel Uctas, Senior Consultant at ResourceWise Chemicals, considers the past year and provides some indicators for 2025.
Plasticizer Market Drivers in 2024
Key oxo-chemicals manufacturer OQ Chemicals declared force majeure on 2-EH following a fire at a syngas unit operated by French company Air Liquide's Oberhausen, Germany site on February 27.
The halt in synthesis gas production led to supply constraints on 2-EH and various other products that OQ Chemicals produces at Oberhausen. 2-EH availability tightened significantly in March following OQ Chemicals' force majeure declaration. The move sent spot values for 2-EH shooting up dramatically, although formula-based volumes remained linked to propylene and natural gas costs.
For other European 2-EH producers, OQ Chemicals' problems—along with the subsequent tightness in the market and rising prices—heralded a better 2024 than anticipated. Expectations for demand driven by the key downstream sectors, including plasticizers and 2-EHA, had been low. 2-EH prices, however, went up from February 2024, though they reversed direction in May.
Market Drivers for Key Plasticizer DOTP
As shown in the graph below, European DOTP prices rose in Q1, as did the North American index Industrial Accounts DDP. However, Europe's price index exhibited a downward trend for most of the remainder of the year. This reflected the soft demand picture in key downstream industries. Also, the relaxation of the 2-EH market after OQ Chemicals lifted its force majeure declaration is reflected in the downward spiral.

The diverting of shipping routes from the Red Sea to longer routes via the Cape of Good Hope led to an increase in prices for imported DOTP from South Korea due to higher freight rates. OQ’s force majeure led to a sharp increase in 2-EH costs.
Turkish DOTP producers also faced very high 2-EH costs from suppliers both in Europe and elsewhere, exacerbated by higher freight costs. Later in the year, with the increased capacity additions of 2-EH in China and a long US market, Turkish producers were able to benefit from lower 2-EH import prices.
By contrast, European producers tended to struggle to compete with these low prices, especially given the uptrend in natural gas prices in Europe during the winter months.
Europe Outlook: Plasticizers in 2025
There is no sign of an improvement in European downstream 2-EH derivative markets in 2025, with the slow construction industry offering no impetus for positive change in PVC demand. During 2024, the long force majeure at OQ Chemicals offered opportunities to other producers who had a reasonably good first half of the year.
However, 2025 may prove to be more difficult for the industry, especially given the huge 2-EH capacity increases in China and modest demand growth expectations in the Asian market.

For plasticizers, 2025 is expected to be another challenging year with no sign of an upturn in demand. Its key sector, construction, is likely to remain subdued, while the automotive sector is also facing a challenging market environment. The expectation of a soft 2-EH price trend in Asia could mean that Asian DOTP prices maintain a competitive edge in Europe. Overall, the European market is forecast to be well supplied, with a similar flavor to 2024’s market performance.
US Protectionism and Markets
The US plasticizer market has had a better year than the Europeans. However, demand, especially in the second half of the year, was stymied by the ongoing high interest rates, which have been besetting the housing market and holding back house purchases. Offtake in the automotive industry was quite stable in 2024, and a similar trend is forecast for 2025.
In March, Tennessee-based Eastman Chemical Company initiated an anti-dumping probe into European and Asian exports.
Preliminary results from the US Department of Commerce’s investigation imposed substantial duties on imports from Turkey (61.61-80.71%) and Poland (57.8%). Lesser duties, however, were imposed on imports from Taiwan (18.73-32.94%) and Malaysia (6.97%).
This has already had an impact on the US market as it has discouraged imports from the affected countries to the benefit of domestic producers Eastman and BASF. Buyers will have a limited choice of DOTP supply in 2025, and some fear that domestic producers may take the opportunity to increase margins.
Overall, US 2024 plasticizer prices remained fairly stable but with minor fluctuations here and there. Only the TOTM market was excepted, where product prices were driven by soaring feedstock costs.
Before a Force Majeure...
In March 2024, Ineos declared force majeure on trimellitic anhydride (TMA) leading to a rapid tightening of TOTM supply in North America. Later in April Ineos announced the permanent closure of its Joliet, Illinois TMA production, citing the raw material outlook and the TMA/TOTM global supply position.
The move put enormous pressure on the TMA/TOTM market globally, with prices in all regions shooting upwards as TOTM producers sought alternative TMA sourced from China.
The European market does have local TMA production—namely, Polynt's product—but the European market was, previously at least, partially reliant on US imports. 2025 will remain a challenging year, but there are signs that the US TOTM market is softening somewhat in early 2025 as the market stabilizes.
Another key feedstock for phthalate plasticizers, phthalic anhydride (PA) will see a structural change in the US market, with one of the two domestic producers Koppers, announcing the planned shuttering of its Stickney, Illinois PA plant.
In view of the limited expectation for plasticizers demand in 2025, domestic PA production may be more or less sufficient to cover demand this year, and the full impact of the closure may not be evident until next year.
China Prices: A Rise and Tumble Scenario
Chinese DOTP prices have followed closely in line with the trend in 2-EH prices which rose rapidly in late 2023, peaking at $1618/ton ex-works in January before tumbling back down and following a largely downward trend for the remainder of the year with brief spikes in June and October.
This reflected the lackluster demand picture in China, which failed to reanimate throughout the year and consequently weighed on the Asian market. Producers in South Korea, meanwhile, faced high freight costs for exports of DOTP into the key European market.
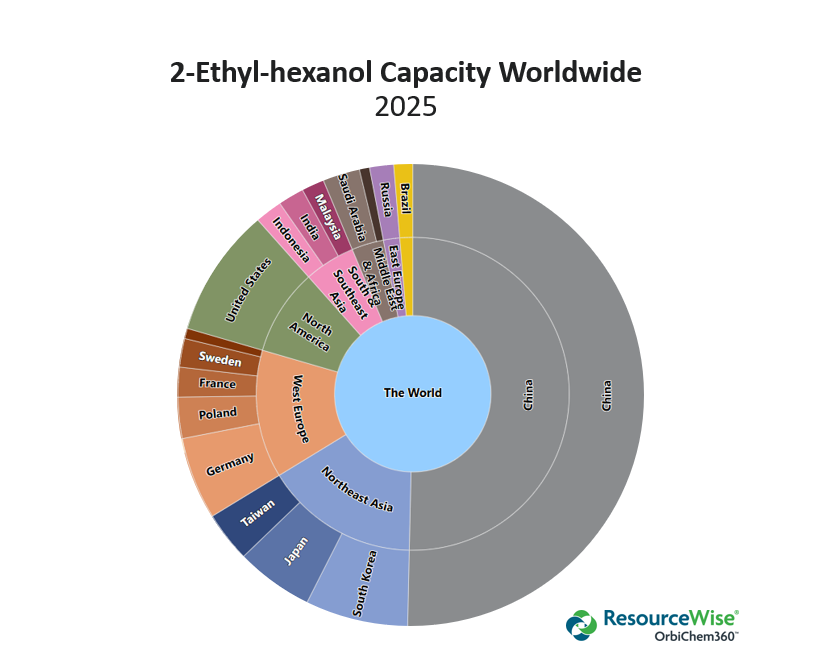
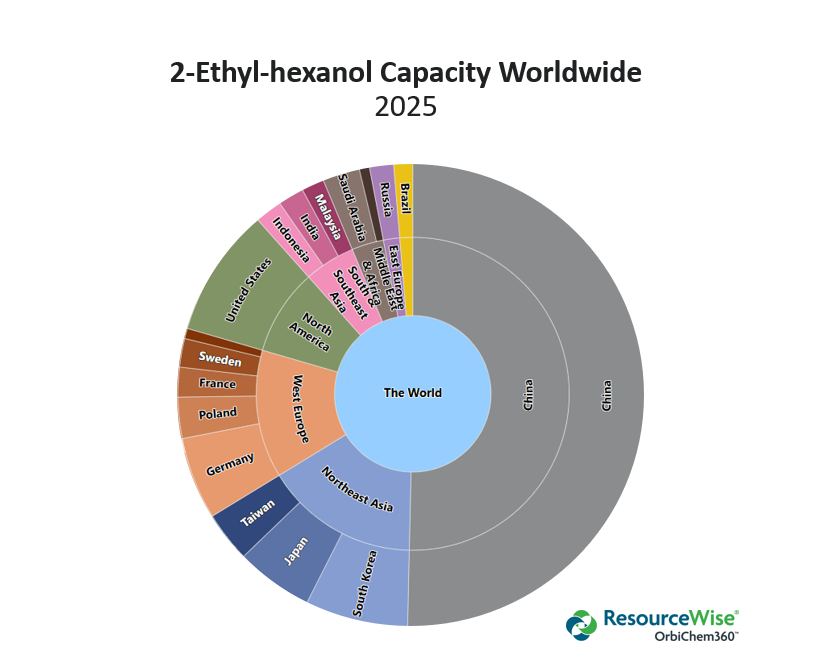
While remaining a net importer of 2-EH in 2024, China exported a significant volume of 2-EH in 2024, reflecting the country's increased production. From January to November 2023, China exported 9,639 metric tons (mt) 2-EH to the UAE. However, during the same period in 2024, China exported a total of 68,382 mt. As is shown in the interactive graphics within the Trade dashboard of OrbiChem360, 29,363 mt went to India, 25,825 mt went to the United Arab Emirates, and 13,194 went mt to Turkey.

2-Ethylhexanol Glut Looming Large?
China’s 2-EH capacity will continue to expand significantly in 2025 with the planned startup of new capacities amounting to 870ktpa, although some new plant startups could eventually be delayed.
China’s 2-EH production increase is expected to exceed demand growth from plasticizers in 2025, which will lead to a decrease in 2-EH import volume. There has been some capacity rationalization in South Korea, with LG closing one of its 2-EH though likely insufficient to halt a downward trend in pricing.
Chinese plasticizer capacity could expand slowly in 2025. Although demand for plasticizers will improve slightly, the market is expected to continue to face oversupply. As a result, plasticizer prices may soften in reflection of the trend in 2-EH prices in 2025.
In addition, the long-awaited and delayed start-up of oil and gas company Petronas’ new isononanol (INA) facility in Malaysia finally happened in the second half of 2024. Though it isn't yet clear how the new plant is currently running, the site is likely to ramp up and exert some downward pressure on the Asian DINP market price. It will certainly bring a more competitive element to the Asian INA—and, therefore, DINP—market, with a potential impact on international markets, too.
In Europe, Evonik Oxeno announced the expansion of its INA-based DINCH and DINCD plasticizers. Although a specific timeline and capacity were not officially confirmed, work was reported to begin in 2024. Czech Republic-based producer Deza is also planning an increase in its plasticizers capacity, which is due to come onstream, moving capacity from 50 to 70ktpa. This will necessitate the closure of its DINP plant from June to September 2025.
This temporary constraint in European supply could support the DINP market in 2025 to a limited extent, although demand is unlikely to improve in the short to medium term, and no significant impact is expected to be felt.
Tariffs on Horizon
The US DINP and DPHP market awaits to see whether any new tariffs come into play in 2025. The Trump administration may impose tariffs on imports of plasticizers from Europe, which could impact imports of DINP and DPHP from Europe, but perhaps other regions.
There may also be tariffs imposed on end products. Demand in the US is forecast to be largely stable for the first half of 2025, with the possibility of some upside in the second half, although many uncertainties remain. A recent regulatory announcement regarding the safety of DINP and DIDP in most applications is likely to go some way to supporting the industry.
The US Environmental Production Agency released its findings in January into a producer-requested investigation into both DINP and DIDP plasticizers. The investigation was initially requested in 2019, and the report concludes that uses of DINP and DIDP regulated under TSCA do not pose an unreasonable risk of injury to human health for consumers, the general population, or the environment.
Explore plasticizers, potential human health implications, and the regulatory landscape around them in our blog post, An Investigation of Plasticisers in 21st Century Value Chains.
Stay updated on these trends and market insights in wider chemical sectors by subscribing to our newsletter or exploring our latest commodity reports.

 Jane Denny
Jane Denny


![[Video] Molecules to Markets Episode 1: Chemical Markets Begin 2026 in a Supply-Driven, Margin-Sensitive Environment](https://www.resourcewise.com/hubfs/images-and-graphics/blog/chemicals/2026/weekly-video-series-molecules-to-markets/CHEM-Weekly-Video-Series-Molecules-to-Markets-Episode-1.png)
