5 min read
Maleic Anhydride Markets: Review 2024 and 2025 Outlook
 Jane Denny
:
Jan 22, 2025 12:00:00 AM
Jane Denny
:
Jan 22, 2025 12:00:00 AM
Demand for maleic anhydride from downstream sectors—including automotive, construction, and electronics, as well as the crucial unsaturated polyester resin market—remained weak in 2024.
Disruptions to output due to unplanned outages, shutdowns, and maintenance activity temporarily tightened supply, which created a more balanced market.
Ongoing conflict in the Red Sea increased freight costs and insurance premiums but also exacerbated shipping delays. Amid this scenario, recovery was slow and a general economic flatness pervaded global markets.
Kaiyin Hu, Senior Consultant at ResourceWise Chemicals, observed that "2024 remained a difficult year for the global MA market."
Maleic Anhydride Market Drivers in 2024
 High interest rates continued to dampen consumer spending. UPR, the biggest end-use sector of MA, saw volumes shrink further in the US in 2024 versus 2023. This was primarily driven by a collapse in marine demand alongside a stagnant housing sector.
High interest rates continued to dampen consumer spending. UPR, the biggest end-use sector of MA, saw volumes shrink further in the US in 2024 versus 2023. This was primarily driven by a collapse in marine demand alongside a stagnant housing sector.
"In Europe, the situation is similar or even worse, with the automotive industry slipping deeper into crisis by the end of 2024. MA producers struggled with limited or even negative margins amid fierce competition in Asia.
"Elevated shipping costs and prolonged shipping times reduced the competitiveness of Asian materials in other regions. Customers in Europe and North America sought domestic supply," Hu adds.
Towards the end of 2024, planned and unplanned outages of MA plants in Europe created a brief shortage in the market and pushed MA prices up to their highest levels of the year despite overall demand remaining weak. As domestic supply is gradually being restored in the New Year, MA prices are expected to ease back and stabilize.
The graph above (click image to open in a new window) shows the regional variations, as well as the ebbs and flows that characterize price MA price indexes globally.
Firstly, it should be noted how significant the price gap between the highest price point for MA sold—in North America—and the lowest price at which it was sold globally—namely in China.
In H1, the North American Molten Spot trade price was, at times, well in excess of 200 percent higher than China's EXW product. As the year ended, the gap between the most expensive—West Europe Solid Spot—and the least expensive—still China's Domestic EXW—had narrowed. However, a relatively small drop in the Chinese product's price—or conversely, a similar percentile rise in the Western Europe or North American price—would tip the disparity beyond a thousand dollars.
For many commodity products, such east versus west price disparity present arbitrage opportunity. However, logistics and shipping issues, such as the Red Sea problems, are currently creating a barrier to profitable business deals of this type. Even if the transportation and logistical issues eased, the North American MA market would remain relatively closed to imports from China due to high tariffs. In fact, the North American MA market is intensely regional.
Overcapacity: Piling Pressure on Profit
In 2024, a total of 1460 ktpa new capacities of MA came onstream in China, representing all global capacity gains for the year. Over half of this new capacity— 840 ktpa—belongs to Hengli Petrochemical, which has integrated downstream BDO production.
Increased supply of MA has put further pressure on an already oversupplied market, heavily weighing on margins. Many butane-based MA producers in China are already operating close to, or below, production costs. It is estimated that the overall butane-based MA operating rate in China is around 50-60 percent. Meanwhile, all benzene-based MA producers remained offline due to the higher cost of benzene.
A further 2,500 ktpa of new MA capacity is scheduled to come online in China, most with downstream 1,4 butanediol (BDO) capacity integrated. However, current low BDO market prices combined with the relatively high cost of production presents a major barrier to the successful start-up of the MA-based BDO plants.
The graph below (click image to open in a new window) shows China' BDO prices are the lowest globally, although the price gap between China's Import (CFR) and West Europe's contract narrowed significantly toward the end of 2024.

Price fluctuations for BDO are not extreme, nor are they even particularly obvious. Hu believes that "most of the correction after the Covid boom has already happened. That process happened during H2 2022 and through 2023".
"Since then, markets have lacked the pickup factors they have needed. Prices will, therefore, mainly fluctuate slightly in line with feedstocks or freight price volatility, or, in some cases, supply issues," Hu adds.
 Despite the trend for low run rates even at China's established UPR plants, new capacities are at the planning stages.
Despite the trend for low run rates even at China's established UPR plants, new capacities are at the planning stages.
Run rates at established facilities have trended around the 40-45 percent mark for some time but are currently as low as 25 percent due to the Chinese New Year approaching.
Jane Zhu, Consultant ResourceWise Chemicals, (pictured left) is based in China. Zhu says around 900 ktpa of new UPR capacity had been earmarked to come onstream this year. However, she notes, the actual new capacity we are likely to see released is unlikely to reach 60 percent of the total new output planned for 2025.
Key Maleic Anhydride Market Movements
- Taiwan's Nan Ya Plastics Corporation suspended MA operations in Q4 2024 citing "difficult market conditions" with no clarity on when production may restart
- Argentina’s YPF exited the MA business at the end of 2024
- Brazil's Elekeiroz is now South America's sole MA producer
- The closure of Nan Ya and YPF's MA facilities will likely provide opportunity for other MA suppliers.
Maleic Anhydride Market Outlook for 2025
The policies and levers the new US president, Donald Trump, chooses to push or pull— especially those related to trade—will greatly impact market dynamics. Geopolitical tensions remain, and market uncertainty has ramped up, Hu adds.
"In the US, the risks for higher inflation will likely increase due to the potential change in trade policy under the new Trump government. There are also concerns about how new tariffs and potential counter-tariffs on different products along the value chain could impact MA demand. This is making it harder for customers to assess their demand for 2025.
"In Europe so far, there have been no positive signals that the economy will see a real pickup in 2025. In fact, market participants are more cautious amid geopolitical instability.
"In China, people are pinning their hopes on the Government’s economic stimulus policies. There were recent reports that second-home trading activity was stimulated by the Chinese government's Q4 macroeconomic policy shifts.
Trump’s tariffs could potentially cause a major shift in global maleic anhydride trade flow in 2025. The impact of this remains to be seen.
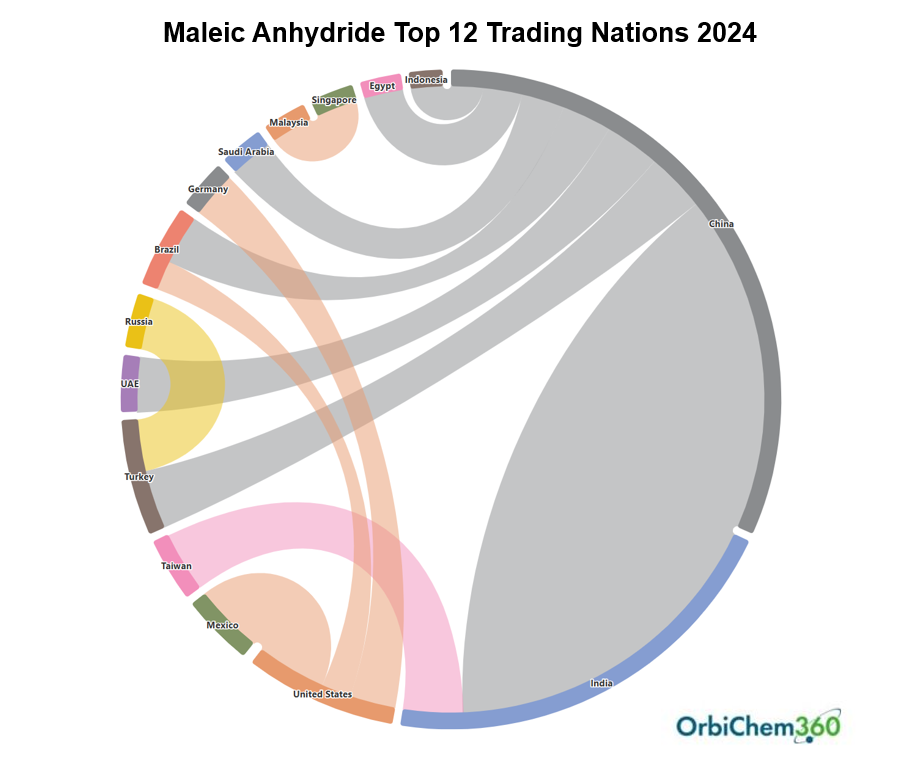
Reviewing 2024 Trade Flows
The Trade dashboard in our chemical data and analysis business intelligence platform OrbiChem360 draws datasets from Global Trade Tracker (GTT). Swiss information services provider GTT—said to cover 99% of the world's official trade statistics—analyzes and shares insight in real-time.
ResourceWise servers convert GTT's 30,000-plus data points to user-friendly interactive visuals each week. The import and export datasets on which it relies are subject to a time lapse, although some countries report as rapidly as within five weeks. This means that the graphs below may update in the coming weeks, although it is unlikely dynamics will be altered at this stage.

As the graph above shows, China's exports to Türkiye are substantial. The country's downstream producers represent China's third-largest export market. West Europe reduced its MA imports in 2024. This was because buyers sought supply from domestic producers amid logistics constraints. It appears South Korean producers took the greatest hit from the change in fundamentals, with its exports to West Europe around half what they were in 2023. Taiwan and Malaysia also suffered due to last year's shake-up of trade flows. Very likely, it was Chinese producers that usurped these countries' markets.

As shown in the graph below, Russia continued to replace China in Türkiye as the major MA supplier. In 2022, Russia exported less than 3 kilotons of MA into Türkiye. The following year, it was close to 20 kilotons. Then, in 2024, it was edging closer to the 30 kilotons mark.
China's MA exports to Türkiye, meanwhile, effectively halved year-over-year.
If petroleum refineries company Tatneft starts up its new MA plant in Türkiye according to plan this year, Türkiye— which has been relying 100 percent on imports of MA—will see a significant reduction in imports as they are replaced by domestic production.
It will mean that current suppliers of MA to Türkiye—which include Russia and China—will have to find alternative export markets such as India, South America and the Middle East.

As shown in the graph below, Brazil's import of MA remained at a high level in 2024. This trend, however, may be about to change. In October 2024, Brazil practically doubled its import tariffs on MA to 20 percent. The move—which will remain in place through mid-October 2025—aims to reduce imports and boost domestic MA output.
Maleic Anhydride Markets: Final Thoughts
While 2024 saw pockets of opportunity for some producers, significant growth remained elusive. With more MA coming onstream in the coming year, a pick up in business will be vital to assuring markets remain viable.
Stay updated on these trends and market insights in wider chemical sectors by subscribing to our newsletter or exploring our latest commodity reports.







![[Video] Molecules to Markets Episode 2: Electrification, Interest Rates, and Emerging Chemical Market Upside](https://www.resourcewise.com/hubfs/images-and-graphics/blog/chemicals/2026/weekly-video-series-molecules-to-markets/CHEM-Weekly-Video-Series-Molecules-to-Markets-2-CHEMICAL%20PRODUCTS%20SOCIAL%20SPEAKER%20HIGHLIGHT.png)