Budgets are financial plans that play a crucial role in the success and profitability of businesses. For companies that rely on raw materials as inputs for their products or services, planning and budgeting for direct materials purchases is a critical component of overall budgeting. This blog post will explore the importance of a direct materials budget, its benefits, and the key steps in effectively planning and budgeting for direct materials purchases.
What is a Direct Materials Budget?
A direct materials budget outlines the estimated quantities and costs of the materials needed to meet planned production targets. It is a vital component of overall budgeting and plays a significant role in a business's operational efficiency and profitability.
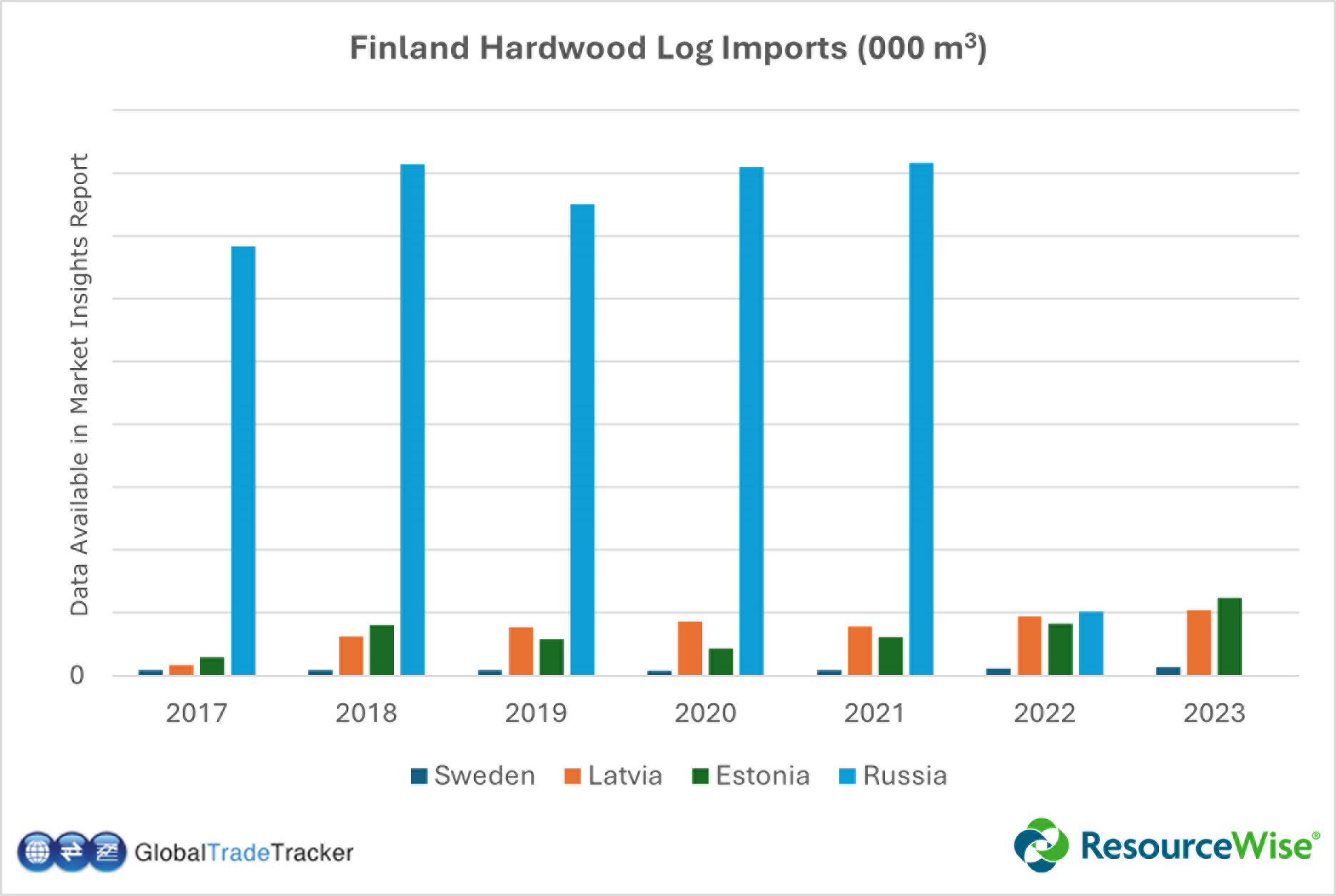
The direct materials budget typically includes a detailed breakdown of the various materials necessary for production, such as chemicals, timber, wood pulp, and waste vegetable oil. It accounts for factors such as anticipated production volumes, inventory levels, supplier pricing, material availability, lead times, and expected fluctuations in material costs.
What are the Benefits of a Direct Materials Budget?
By accurately forecasting and planning for raw material needs, companies can optimize inventory levels, prevent shortages or excesses, and negotiate better pricing with suppliers. A well-structured direct materials budget helps businesses ensure a smooth production process, minimize waste, and maintain consistent product quality. Direct materials budgets also help companies effectively manage:
- Cost Control: By accurately estimating and managing the costs associated with forest product raw materials, companies can plan and allocate financial resources, control expenses, and avoid unexpected financial burdens.
- Profitability: To optimize profitability, companies need to ensure that the cost of raw materials is accurately factored into pricing strategies. Companies can set competitive prices by understanding and budgeting for raw material costs while maintaining healthy profit margins.
- Supply Chain Stability: Direct materials are critical to many companies' supply chains. By budgeting for these materials, companies can ensure a steady supply and reduce the risk of disruptions or shortages, maintaining production schedules and meeting customer demands.
- Sustainability and Responsible Sourcing: Budgeting allows companies to incorporate sustainability practices into their procurement strategies. By allocating funds for responsibly sourced raw materials, companies can contribute to conservation efforts, promote ethical practices, and enhance their brand reputation.
In addition, the direct materials budget serves as a basis for analyzing the overall financial feasibility of production plans, assessing the impact of price changes or supply disruptions and making informed decisions regarding sourcing strategies or alternative materials.
Understanding Direct Material Needs
To begin budgeting, businesses must thoroughly understand the direct materials they need. This involves assessing the types of materials necessary for production, analyzing quantity and quality requirements, and evaluating seasonal variations and supply and demand fluctuations. By clearly understanding these factors, companies can effectively plan their budget and avoid shortages or surpluses that could impact profitability.
Researching and Sourcing Direct Materials
Comprehensive market research is essential once the direct material needs are determined. Companies should explore available suppliers and their offerings, considering reliability, quality, and sustainability. Evaluating the environmental impact of different suppliers is crucial in promoting responsible sourcing practices. Organizations can secure a stable supply chain and optimize cost management by negotiating favorable pricing and establishing long-term contracts with reliable suppliers.
Cost Estimation and Forecasting
Businesses rely on various data sources to provide valuable insights into market dynamics, historical purchasing patterns, supplier relationships, and internal demand forecasts. By harnessing these data sources, companies can make informed decisions, accurately forecast direct materials requirements, negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, and develop accurate budgets. Some of these data sources include:
- Historical Purchase Data: Analyzing historical purchase data is a valuable source of information for companies. It helps identify trends, seasonality, and patterns in direct materials purchases, enabling better forecasting and budgeting.
- Inventory Management Systems: Companies can use inventory management systems to track direct materials usage and stock levels. This data provides insights into consumption rates, lead times, and reorder points, facilitating more accurate planning and budgeting.
- Supplier Data: Companies can gather data from their suppliers, such as pricing information, lead times, and contractual agreements. Understanding supplier capabilities and constraints helps negotiate favorable terms, estimate costs, and plan for direct materials procurement.
- Market Research and Industry Reports: External sources like market research reports, industry publications, trade associations, and business intelligence platforms provide valuable data on market trends, price fluctuations, and availability of direct materials. This information assists in making informed decisions about sourcing and budgeting.
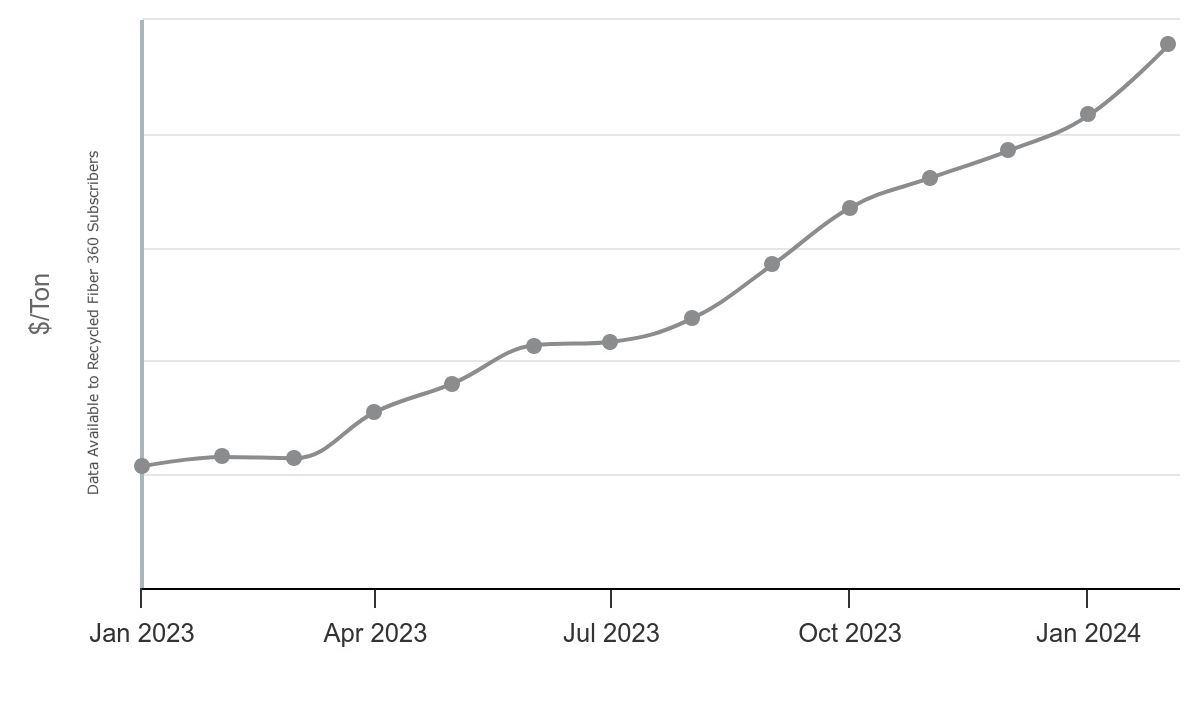
- Economic Indicators: Monitoring economic indicators, such as inflation rates, currency exchange rates, and commodity prices, can provide insights into the cost of direct materials. These indicators help companies anticipate and budget for price fluctuations and market volatility.
- Internal Sales Forecasts: Collaboration between sales and procurement teams is essential. Sales forecasts, customer demand data, and product development plans help estimate future direct materials requirements, allowing for more accurate budgeting and planning.
- Supplier Performance Data: Companies can track and evaluate supplier performance metrics, including delivery reliability, quality, and responsiveness. This information helps assess suppliers' reliability and efficiency, influencing budgeting decisions related to direct materials procurement.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Analysis: Analyzing the cost breakdown of finished goods, including the proportion attributed to direct materials, provides insights into the impact of material costs on overall profitability. This analysis aids in setting appropriate budget targets for direct materials expenses when planning and budgeting for direct materials purchases. Tools and software that provide accurate and timely information on historical patterns, market trends, and future predictions can significantly enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of the process.
Direct Materials Budget Format and Calculations
Let's look at a sample direct materials budget. To keep this illustration simple, we'll use a mono-material product. A hypothetical company, Knots & Grains, produces wooden kitchen tools such as cutting boards and cooking utensils. They are creating a monthly direct materials budget for their line of maple cutting boards. Here's what their three-month budget might look like.
Knots & Grains
Direct Materials Budget
|
|
Month 1 |
Month 2 |
Month 3 |
|
Production Units |
250 |
300 |
500 |
|
Direct Materials Per Unit (1”x4”x3’ Maple Boards) |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
|
Direct Materials Needed for Production |
375 |
450 |
750 |
|
Add: Desired Direct Materials Ending Inventory |
150 |
100 |
75 |
|
Total Direct Materials Needed |
525 |
550 |
825 |
|
Less: Beginning Direct Materials Inventory |
200 |
150 |
100 |
|
Cost per Unit of Direct Materials |
$60 |
$60 |
$60 |
|
Total Cost of Direct Materials Purchases |
$19,500 |
$24,000 |
$43,500 |
Working from the top to the bottom of the table, these are the values and calculations you’ll need to know for each period, whether you’re preparing this budget monthly or quarterly.
DIRECT MATERIALS NEEDED FOR PRODUCTION
|
Production Units |
x |
Direct Materials Per Unit |
= |
Direct Materials Needed for Production |
TOTAL DIRECT MATERIALS NEEDED
|
Direct Materials Needed for Production |
+ |
Desired Direct Materials Ending Inventory |
= |
Total Direct Materials Needed |
TOTAL COST OF DIRECT MATERIALS PURCHASES
|
(Total Direct Materials Needed - Beginning Direct Materials Inventory) |
x |
Cost per Unit of Direct Materials |
= |
Total Cost of Direct Materials Purchases |
Assessing the Risk Factors
Direct materials procurement involves various uncertainties that can impact both cost and availability. By conducting a comprehensive risk assessment, businesses can identify potential challenges, such as price fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, and quality issues. This evaluation enables proactive planning and the implementation of strategies to mitigate these risks, ensuring a stable and efficient direct materials budgeting process. By staying vigilant and addressing the risk factors head-on, companies can maintain a competitive advantage and safeguard their production operations.
Monitoring and Managing Inventory
Efficient inventory management is key to successful budgeting for raw materials. Implementing robust systems to minimize waste and losses enables organizations to optimize resource utilization. Tracking raw material usage, inventory levels, and replenishment timelines ensures that companies have the right amount of materials at the right time.
Budget Review and Analysis
Regularly reviewing and analyzing the budget performance related to raw material expenses is critical for continuous improvement. Companies should identify areas of improvement, cost-saving opportunities, and potential optimizations. Adjusting the budget and strategies based on feedback, changing market conditions, and business goals allow organizations to adapt and stay competitive in a dynamic industry.
Get our free tip sheet, 5 Common Direct Material Purchasing Risk Factors and How to Address Them.


 Angela Rockwell
Angela Rockwell